این آموزش به صورت متعادل و با استفاده از ترمودینامیک، رفتار جامدات و مایعات را بررسی می نماید. در این آموزش همچنین مطالب ریاضیات پیشرفته جهت فهم بهتر فصل های اولیه کتاب ارائه شده است. این آموزش مشتمل بر 150 تمرین و همچنین حاوی مثالهای کاربردی زیادی می باشد...
محصولات مرتبط
این آموزش به صورت متعادل و با استفاده از ترمودینامیک، رفتار جامدات و مایعات را بررسی می نماید. در این آموزش همچنین مطالب ریاضیات پیشرفته جهت فهم بهتر فصل های اولیه کتاب ارائه شده است. این آموزش مشتمل بر 150 تمرین و همچنین حاوی مثالهای کاربردی زیادی می باشد.
مقدمه ای بر مکانیک محیط های پیوسته (Introduction to Continuum Mechanics) مشتمل بر 252 صفحه، در 14 فصل، با فرمت PDF، به زبان انگلیسی، همراه با مثال ها و تمرینات متعدد به ترتیب زیر گردآوری شده است:
Chapter 1: Introduction
- Concept of a Continuum
- Sequence of Topics
Chapter 2: Cartesian Tensors
- Index Notation and Summation Convention
- Kronecker Delta and Permutation Symbol
- Example: Skew Symmetry
- Example: Products
- Coordinate System
- Coordinate Transformations
- Vectors
- Tensors
- Examples of Tensors
- Quotient Rule
- Inner Products: Notation
- Quadratic Forms and Eigenvalue Problems
- Example: Eigenvalue Problem
- Diagonalization and Polar Decomposition
- Example: Polar Decomposition
Chapter 3: General Tensors
- Vectors and Tensors
- Physical Components
- Tensor Calculus
- Curvature Tensors
- Applications
- Example: Incompressible Flow
- Example:Equilibrium of Stresses
Chapter 4: Integral Theorems
- Gauss Theorem
- Stokes Theorem
Chapter 5: Deformation
- Lagrangian and Eulerian Descriptions
- Deformation Gradients
- Deformation Gradient Vectors
- Curvilinear Systems
- Strain Tensors
- Decomposition of Displacement Gradients
- Stretch
- Extension
- Infinitesimal Strains and Rotations
- Deformation Ellipsoids
- Polar Decomposition of the Deformation Gradient
- Stretch and Rotation
- Example: Polar Decomposition
- Example: Square Root of a Matrix
- Logarithmic Strain
- Change of Volume
- Change of Area
- Compatibility Equations
- Spatial Rotation and Two-Point Tensors
- Curvilinear Coordinates
Chapter 6: Motion
- Material Derivative
- Some Terminology
- Example: Path Line, Stream Line, and Streak Line
- Length, Volume, and Area Elements
- Length
- Volume
- Area
- Material Derivatives of Integrals
- Line Integrals
- Area Integrals
- Volume Integrals
- Deformation Rate, Spin, and Vorticity
- Strain Rate
- Rotation Rate of Principal Axis
Chapter 7: Fundamental Laws of Mechanics
- Mass
- Conservation and Balance Laws
- Conservation of Mass
- Balance of Linear Momentum
- Balance of Angular Momentum
- Balance of Energy
- Entropy Production
- Axiom of Material Frame Indifference
- Objective Measures of Rotation
- Integrity Basis
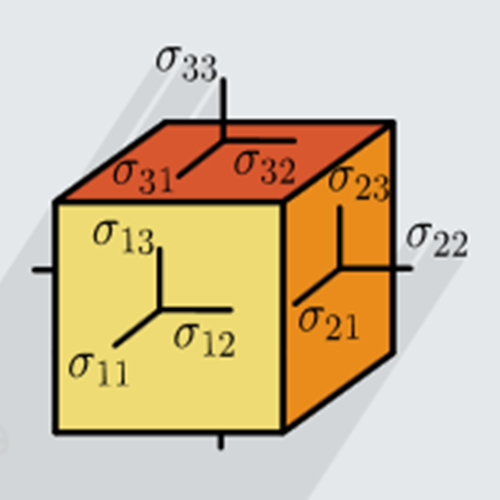
Chapter 8: Stress Tensor
- External Forces and Moments
- Internal Forces and Moments
- Cauchy Stress and Couple Stress Tensors
- Transformation of the Stress Tensor
- Principal Stresses
- Shear Stress
- Hydrostatic Pressure and Deviatoric Stresses
- Objective Stress Rates
- Local Conservation and Balance Laws
- Conservation of Mass
- Balance of Linear Momentum
- Balance of Moment of Momentum (Angular Momentum)
- Material Description of the Equations of Motion
- First Piola–Kirchhoff Stress Tensor
- Second Piola–Kirchhoff Stress Tensor
Chapter 9: Energy and Entropy Constraints
- Classical Thermodynamics
- Balance of Energy
- Clausius–Duhem Inequality
- Fourier’s Law of Heat Conduction
- Newton’s Law of Viscosity
- Onsager’s Principle
- Strain Energy Density
- Ideal Gas
- Internal Energy
- Legendre or Contact Transformation
- Surface Energy
- Method of Jacobians in Thermodynamics
Chapter 10: Constitutive Relations
- Invariance Principles
- Principles of Exclusion
- Principle of Coordinate Invariance
- Principle of Spatial Invariance
- Principle of Material Invariance
- Principle of Dimensional Invariance
- Principle of Consistency
- Simple Materials
- Elastic Materials
- Elastic Materials of Cauchy
- Elastic Materials of Green
- Stokes Fluids
- Invariant Surface Integrals
- Singularities
Chapter 11: Hyperelastic Materials
- Finite Elasticity
- Homogeneous Deformation
- Simple Extension
- Hydrostatic Pressure
- Simple Shear
- Torsion of a Circular Cylinder
- Approximate Strain Energy Functions
- Hookean Materials
- Small-Strain Approximation
- Plane Stress and Plane Strain
- Integrated Elasticity
- Example: Incremental Loading
- A Variational Principle for Static Elasticity
- Isotropic Thermoelasticity
- Specific Heats and Latent Heats
- Strain Cooling
- Adiabatic and Isothermal Elastic Modulus
- Example: Rubber Elasticity
- Linear Anisotropic Materials
- Invariant Integrals
Chapter 12: Fluid Dynamics
- Basic Equations
- Approximate Constitutive Relations
- Newtonian Fluids
- Inviscid Fluids
- Shearing Flow
- Pipe Flow
- Rotating Flow
- Navier–Stokes Equations
- Incompressible Flow
- Compressible Flow
- Inviscid Flow
- Speed of Sound
- Method of Characteristics
- Bernoulli Equation
- Invariant Integrals
Chapter 13: Viscoelasticity
- Kelvin–Voigt Solid
- Maxwell Fluid
- Standard Linear Solid
- Superposition Principle
- Constitutive Laws in the Operator Form
- Three-Dimensional Linear Constitutive Relations
- Anisotropy
- Biot’s Theory
- Minimum Entropy Production Rate
- Creep in Metals
- Nonlinear Theories of Viscoelasticity
- K-BKZ Model for Viscoelastic Fluids
Chapter 14: Plasticity
- Idealized Theories
- Rigid Perfectly Plastic Material
- Elastic Perfectly Plastic Material
- Elastic Linearly Hardening Material
- Three-Dimensional Theories
- Postyield Behavior
- Levy–Mises Flow Rule
- Prandtl–Reuss Flow Rule
- General Yield Condition and Plastic Work
- Plane Stress and Plane Strain
- Rigid Plasticity and Slip-Line Field
- Example: Symmetric External Cracks
- Drucker’s Definition of Stability
- Il´ıushin’s Postulate
- Work-Hardening Rules
- Perfectly Plastic Material
- Isotropic Hardening
- Kinematic Hardening
- Hencky’s Deformation Theory
- Endochronic Theory of Valanis
- Plasticity and Damage
- Minimum Dissipation Rate Principle

جهت خرید آموزش Introduction to Continuum Mechanics به مبلغ استثنایی فقط 20000 تومان و دانلود آن بر لینک افزودن به سبد خرید در پنجره بالا کلیک نمایید.
!!لطفا قبل از خرید از فرشگاه اینترنتی برتر فایل قیمت محصولات ما را با سایر محصولات مشابه و فروشگاه ها مقایسه نمایید!!


 فقط پیامک (09010609492)
فقط پیامک (09010609492)












دیدگاه خود را بنویسید